Stop sweating in critical situations!
Diagnosis:
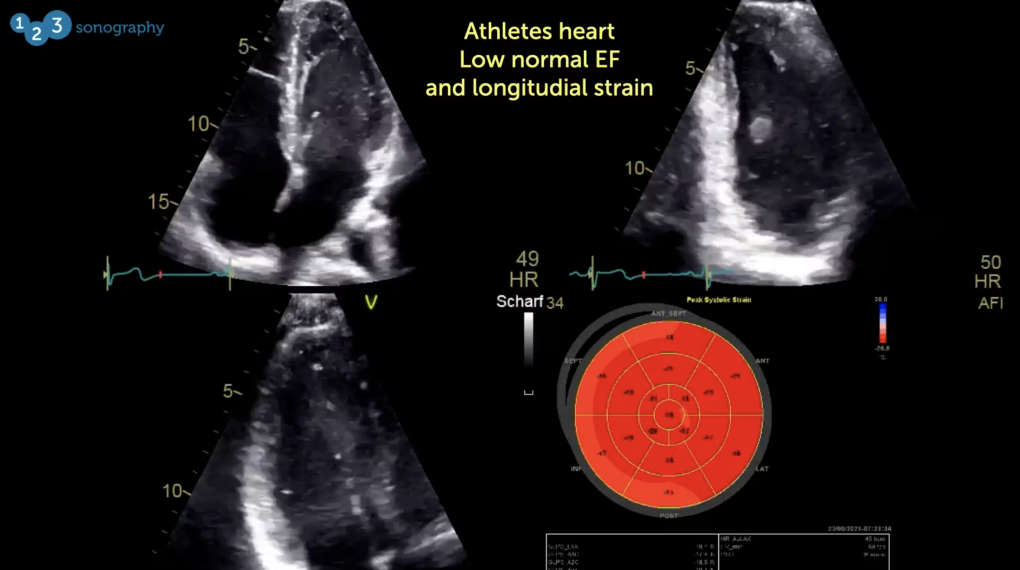
This study shows the typical features of an athlete's heart. The ventricle is enlarged, with a diastolic volume of 156ml above the normal range. The left ventricular function is in the low normal range, with an EF (ejection fraction) of 53%. The global longitudinal strain is low, measuring at -17.1%. In addition, there is eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy.
The form and degree of cardiovascular remodeling depend on the type of athletic discipline and training intensity. Endurance athletes often experience eccentric hypertrophy, which results in increased wall thickness and chamber dilation. On the other hand, strength-trained athletes display thickening of the LV (left ventricular) wall and only mild LV dilation, known as concentric hypertrophy. Soccer is considered an overlap sport, where athletes show a combination of endurance and strength-trained features. The athletic heart typically has increased chamber dimensions and increased LV wall thickness. These findings can often mimic the echocardiographic features of diseases affecting the left ventricle. Low normal ejection fraction can be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or myocarditis, while hypertrophy needs to be distinguished from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or hypertensive heart disease.
While the global longitudinal strain in athletes is usually higher than in patients with hypertrophy for other reasons (hypertrophic CMP or hypertensive heart disease), strain can be mildly reduced, as evidenced in this case.
Did you start sweating when you saw the loop? Beat the heat with our ultrasound courses! Until June 23rd, 2024, with a -30% discount plus Lifetime Access on all courses! 👉 Get yours now!