Chapter 01
Introduction to Carotid Ultrasound
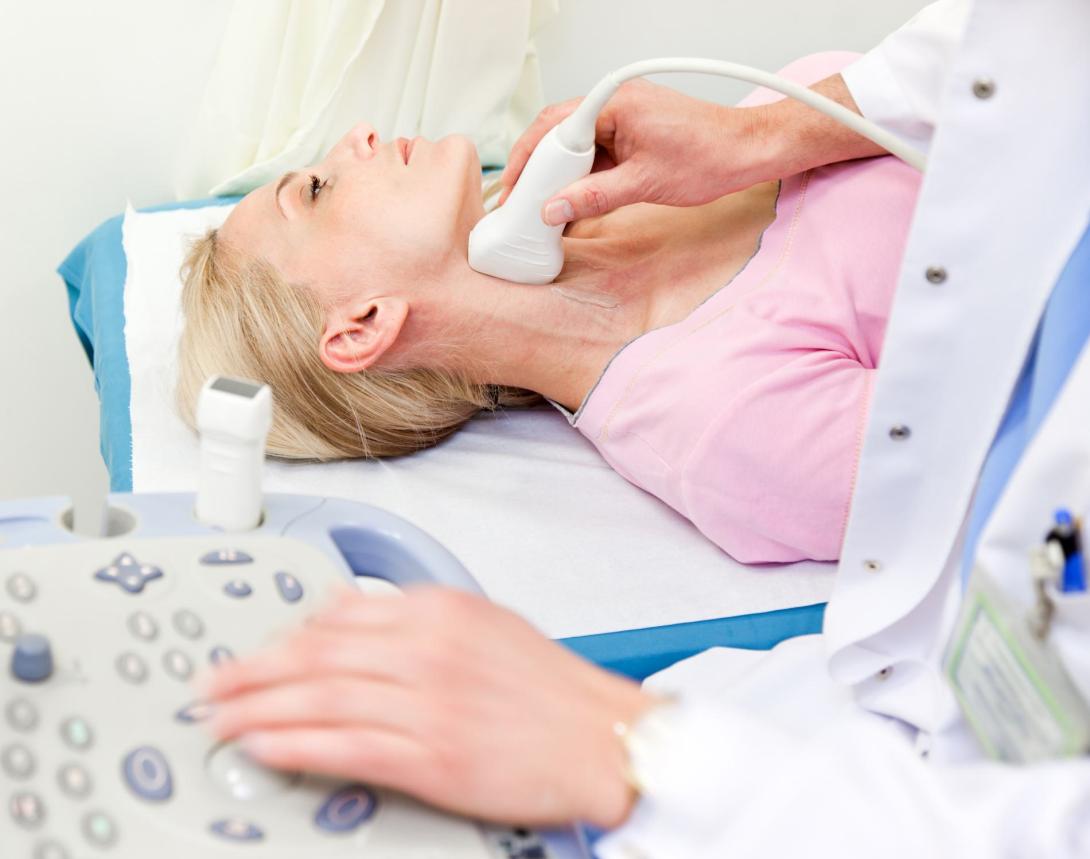
Carotid ultrasound (also called carotid duplex sonography or scan) is one of the most important ultrasound imaging modalities in medicine. It allows us to assess cerebrovascular risk and diseases such as: carotid plaques, carotid artery obstruction (stenosis) and many other pathologies (i.e. dissection, aneurysms, fibromuscular dysplasia)...
Chapter 02
Anatomy
Carotid ultrasound allows you to display the extra cranial vessels of the neck. This includes the carotid arteries and its branches: the internal and external carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries. In addition, we can also see the jugular veins, in particular the internal jugular vein...
Chapter 03
Instrumentation and physical principles
Carotid ultrasound is performed with a linear array probe. Such probes have a large aperture and provide high spatial resolution in the near field. Handheld ultrasound systems have been found to be comparable to mid and high range ultrasound systems (for point of care purposes)...
chapter 04
B mode imaging – Carotid artery
The carotid artery is not very difficult to image. However, to obtain good image quality, it is very important to follow certain rules. Don’t forget: the carotid artery is usually only 1 cm in width, and its branches are even smaller...
chapter 05
Color Doppler imaging of the carotid arteries
Spectral Doppler is part of every standard carotid scan. In carotid ultrasound, we use pulsed wave Doppler. In contrast to continuous Doppler (CW-Doppler), which is mainly used in echocardiography, spectral Doppler allows the measurements of flow velocities within a sample volume...
chapter 06
Spectral Doppler
Spectral Doppler is part of every standard carotid scan. In carotid ultrasound, we use pulsed wave Doppler. In contrast to continuous Doppler (CW-Doppler), which is mainly used in echocardiography, spectral Doppler allows the measurements of flow velocities within a sample volume...
chapter 07
Imaging the vertebral arteries
Imaging of the vertebral arteries is part of a standard extra-cranial cerebrovascular ultrasound duplex scan. The vertebral arteries are smaller, located more distal from the transducer and partially “hidden” behind the bony structures of the vertebrae...
chapter 08
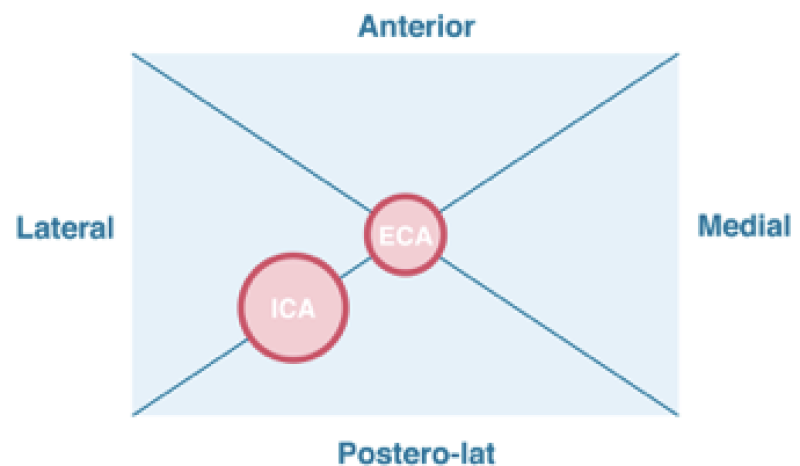
ECA vs ICA - External versus internal carotid artery
One of the most frequently asked questions in carotid ultrasound is: “How can I tell if the vessel I am imaging is the internal- or the external carotid artery?" Especially since the location of the vessels (and their relationship to each other) vary greatly...
chapter 09
Assessment of intima media thickness (IMT)
One of the main indications for a carotid ultrasound scan is the assessment of cerebrovascular risk. The presence of atherosclerotic plaques clearly points to an increased risk (not only for stroke but also for coronary artery disease and peripheral vascular disease)...
chapter 10
Atherosclerotic Plaque
A plaque is a regional thickening of the vessel wall caused by atherosclerosis. Plaques are covered by a fibrous cap and consist of LDL-cholesterol, collagen, smooth muscle cells collagen calcium and different cells (monocytes/macrophages, T lymphocytes, neutrophils and foam cells)...
chapter 11
Carotid Artery Stenosis Part 1
Carotid artery stenosis is defined as a narrowing of the carotid artery, in most cases as the result of atherosclerosis and plaque formation. Carotid artery stenosis (>50%) is present in approximately 5% of the elderly population (>75 years)...
chapter 12
Carotid Artery Stenosis Part 2
Spectral Doppler should be part of every carotid ultrasound exam. It provides important hemodynamic information and is indispensable for the quantification of stenosis. Measurements should only be performed in a longitudinal view...
chapter 13
Vertebral Artery Pathologies
The vertebral arteries contribute 15-25% of the blood supply to the brain (100-200ml). This is significantly less than the carotid arteries. Still, the vertebral arteries (and the vertebro-basilary system) play and important role in the cerebro-vascular circulation...
chapter 14
Subclavian Steal Syndrom
The subclavian steal syndrome is a condition where hypoperfusion of the cerebrovascular system is caused by occlusion (or severe obstruction) of the proximal subclavian or brachocephalic artery...
chapter 15
Carotid Endarterectomy and Stenting
Carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure where the carotid artery is opened, and the plaque is removed. The procedure allows restoration of blood flow and removal of embolic material to reduce the risk of ischemic / embolic stroke and TIA...